 Inflammation isn't just a trendy term; it's a vital part of how our bodies react to injuries and infections. Osteopaths have a deep understanding of inflammation. This blog explores different inflammation types, their effects, and how osteopaths can work with inflammation to promote your body’s healing.
Inflammation isn't just a trendy term; it's a vital part of how our bodies react to injuries and infections. Osteopaths have a deep understanding of inflammation. This blog explores different inflammation types, their effects, and how osteopaths can work with inflammation to promote your body’s healing.
What is inflammation?
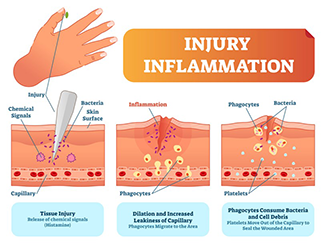
Inflammation is the body's natural response to harmful stimuli, such as injuries or pathogens. It's a complex biological process involving immune cells, blood vessels, and signalling molecules. When triggered, the immune system releases chemicals to protect tissues, resulting in increased blood flow, swelling, heat, and redness—classic signs of inflammation.
Acute inflammation
Acute inflammation refers to inflammation that occurs 1-4 days after an injury. In general, this immune response is quite strong and can be a particularly painful time for patients. This is when many patients come and see their osteo. Acute inflammation is beneficial as it helps the body heal from injuries or fight infections. Once acute inflammation subsides, a patient will usually begin to feel less pain. To ease acute inflammation RICE is recommended (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation). NSAIDS (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory drugs) can also be used in the short term under the guidance of your doctor or pharmacist.
Injury induced chronic inflammation
Allowing acute inflammation to persist for too long after an injury can have detrimental effects, potentially damaging healthy tissues and organs, worsening pain, and impairing function. It is crucial to resolve acute inflammation promptly. While the body typically manages this process efficiently, interventions such as osteopathic treatment can provide valuable assistance.
Disease induced chronic inflammation.
Disease, such as autoimmune disorders or metabolic conditions can also cause chronic inflammation. In these cases, the immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues or responds excessively to perceived threats, leading to sustained inflammation throughout the body. Disease induced chronic inflammation can exacerbate injury induced inflammation, making it more challenging to resolve.
How osteopaths work with inflammation
Osteopathic treatments can create varying levels of inflammation. We do this on purpose as we want to stimulate the body’s own healing system. The extent of inflammation depends on factors such as the intensity and duration of the treatment, as well as individual differences in response. For instance, a joint manipulation may provoke a stronger inflammatory response compared to a gentler technique. An osteopath carefully considers the individual's condition and treatment goals when determining how much inflammation to induce during a session.
Osteopaths can also help reduce inflammation by addressing structural imbalances, enhancing circulation and working with the body's nervous and lymphatic systems. We can also help by providing lifestyle advice. For example, did you know the following have been shown to reduce inflammation?
- Cold therapy
- Stress reduction – for example mediation or spending time with friends
- Including certain foods and spices in your diet such as celery and turmeric
- Avoiding certain foods such as refined carbohydrates and sugary drinks.
If you have any concerns about inflammation, be it injury induced or disease induced, please book in to see one of our Osteopaths to discuss how we can help.
By Monica Bruce
